Why Choose Radiant Heat?
Why Choose Radiant Heat
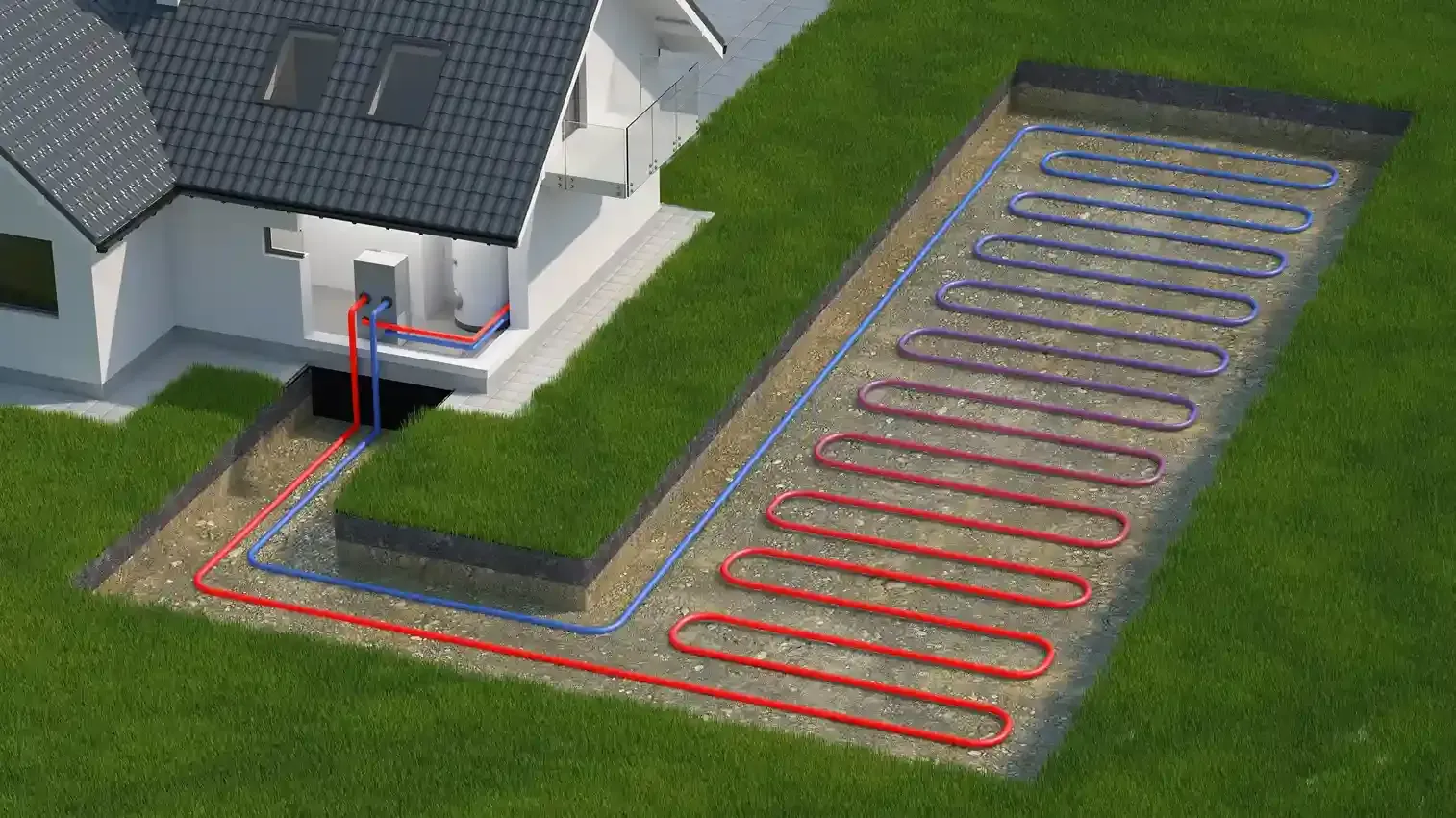
Radiant heat refers to a method of space heating that involves the direct transfer of heat from a warm surface to the objects and people in the room through infrared radiation. Unlike conventional heating systems, which primarily rely on circulating heated air, radiant heating works by directly warming the surfaces of a room. There are various types of radiant heating systems, including those that use electric resistance heating or those that circulate heated water through pipes (hydronic systems), commonly installed beneath floors or within walls.
Applications of Radiant Heat:
Residential Heating:
- Underfloor Heating: Often used in bathrooms, kitchens, and living spaces for a comfortable walking surface.
- Wall Heating: Used in some energy-efficient designs to provide a uniform heat distribution.
Commercial Spaces:
- Offices and Retail: Large open spaces benefit from radiant heating due to fewer drafts and uniform heating.
- Warehouses and Industrial Applications: Radiant heating can be used in areas where localized heat is needed or where forced-air heating would be inefficient.
Outdoor Applications:
- De-icing of Driveways and Walkways: Reduces the need for chemical de-icing methods.
- Stadium Seating: Some outdoor venues use radiant heating to improve comfort for spectators.
Specialty Applications:
- Greenhouses: Offers consistent heat without drying out the air, which benefits plant growth.
- Animal Comfort: Used in veterinary clinics and barns to provide warmth for animals.
Pros of Radiant Heat:
- Comfort: Radiant heating systems often provide a more comfortable indoor environment with fewer cold spots and a more consistent temperature throughout the space.
- Energy Efficiency: When properly installed, radiant heating systems can be more energy-efficient than traditional forced-air systems, especially in well-insulated spaces.
- Improved Air Quality: These systems do not circulate air, reducing the spread of dust, allergens, and other airborne particles.
- Quiet Operation: Without fans or blowers, radiant heating systems operate almost silently.
- Aesthetics: With no radiators, vents, or air ducts, radiant heating allows for greater design flexibility and unobstructed room layouts.
Durability: Hydronic systems, in particular, have long lifespans and require little maintenance.
Cons of Radiant Heat:
- Upfront Cost: The initial installation of a radiant heating system, particularly hydronic systems, can be more costly than conventional systems.
- Installation Complexity: Retrofitting a home with radiant heat can be disruptive and sometimes not feasible, requiring substantial renovation.
- Response Time: Radiant heating systems typically have a slower response time to adjust room temperatures compared to forced-air heating.
- Flooring Limitations: Not all types of flooring are suitable for radiant heating; for instance, thick carpets can insulate the heat.
- Repair Considerations: Repairs, especially for in-floor systems, can be more complex and expensive due to the inaccessibility of pipes or heating elements.
In conclusion
radiant heating systems offer a range of benefits, particularly in terms of comfort and efficiency, and can be applied in various settings, from residential to industrial. While the initial cost and installation complexity may deter some, the long-term energy savings and aesthetic benefits may outweigh these drawbacks for many users. When considering the installation of a radiant heating system, it is essential to weigh these pros and cons carefully and consult with a professional to determine the best system for your specific needs.
We're Listening | Get a free quote today!
Fry - Blog
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.